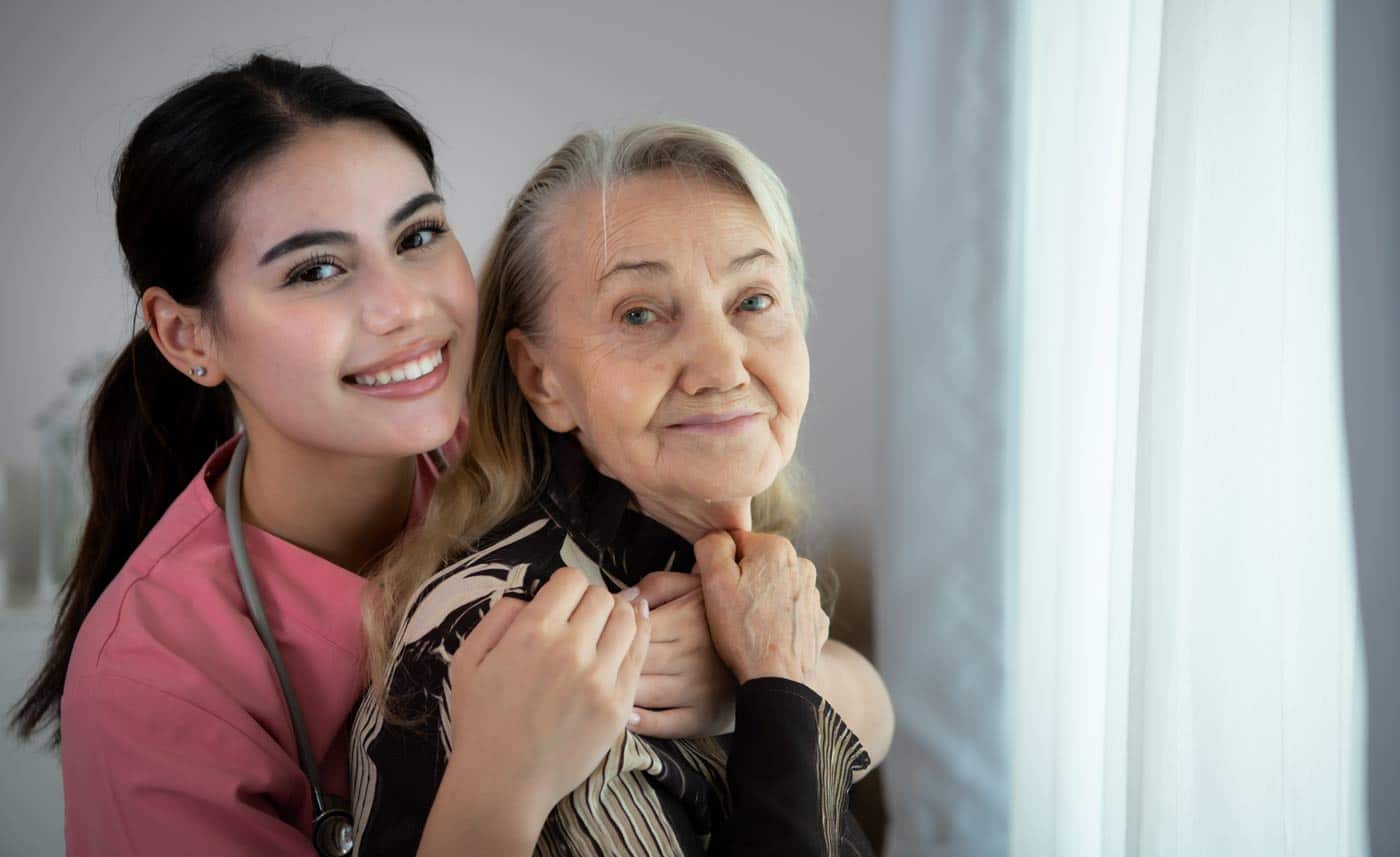
Caregiver Definition
A caregiver is someone who provides assistance to another individual who needs help with daily living activities due to age, illness, disability, or recovery from an injury. Caregivers can be family members, friends, or trained professionals, and their level of involvement varies depending on the needs of the person they are caring for.
Caregivers take on a wide range of responsibilities, from helping with medical needs and personal hygiene to offering emotional support and companionship. Some caregivers provide unpaid care to loved ones, while others work professionally in hospitals, nursing homes, or private home care settings.
Common Caregiver Synonyms
- Guardian
- Carer
- Caretaker
- Health Professional
- Medical Assistant
- Medical Man
- Primary Care Provider
- Nurse
- Medical Practitioner
- Health Care Provider

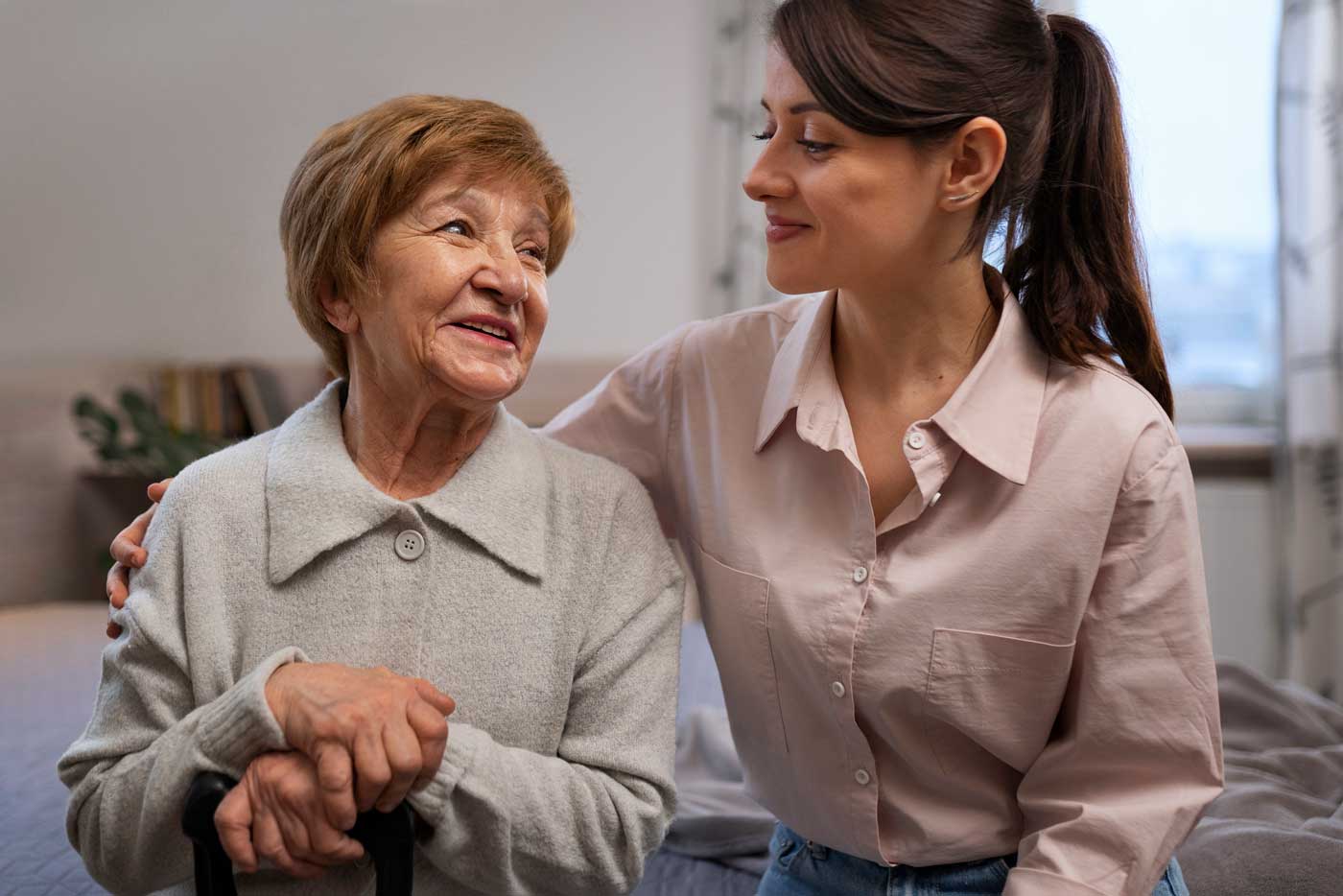
Types of Caregivers
Caregiving is not a one-size-fits-all role. There are different types of caregivers, each with unique responsibilities and challenges.
Family Caregivers
Family caregivers, often unpaid, provide care for relatives or close friends. These individuals step in to assist aging parents, a spouse with a chronic condition, or even a child with special needs. Their work is deeply personal, and while it can be incredibly rewarding, it also comes with emotional and physical challenges.
Common responsibilities of family caregivers include:
- Assisting with bathing, dressing, and meal preparation
- Managing medications and scheduling medical appointments
- Offering emotional support and companionship
- Handling financial and legal matters
Professional Caregivers
Professional caregivers are trained and paid to provide care in homes, hospitals, or long-term care facilities. They include home health aides, certified nursing assistants (CNAs), and personal care attendants.
These caregivers have specialized training to handle medical and non-medical needs, including:
- Administering medications and monitoring health conditions
- Assisting with physical therapy and rehabilitation
- Helping with personal hygiene and mobility
- Providing companionship and social engagement
Volunteer Caregivers
Volunteer caregivers work with community organizations, religious groups, and nonprofit agencies to provide support to individuals who may not have family members available to assist them. While they may not perform medical care, they provide essential services such as:
- Transportation to doctor’s appointments
- Grocery shopping and meal delivery
- Friendly visits and emotional support
Specialized Caregivers
Some caregivers receive additional training to support individuals with specific conditions such as dementia, Parkinson’s disease, or cancer. Specialized caregivers may work in hospice care, providing comfort to individuals in their final stages of life, or assisting people with developmental disabilities in gaining independence.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Caregiver
A caregiver’s role goes beyond simply being present; they are responsible for ensuring the well-being, safety, and emotional health of the person they are caring for. Their duties often include:
Assisting with Daily Living Activities
Caregivers help with essential tasks such as:
- Bathing, dressing, and grooming
- Preparing meals and feeding
- Assisting with mobility and transportation
Providing Medical Care and Health Monitoring
Caregivers often act as a bridge between their loved ones and medical professionals by:
- Administering prescribed medications
- Monitoring health conditions such as blood pressure or blood sugar levels
- Helping with physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises
Offering Emotional and Social Support
Caregiving isn’t just about physical needs—it’s also about emotional well-being. Caregivers help combat loneliness and depression by:
- Engaging in conversations and recreational activities
- Encouraging participation in social groups or hobbies
- Providing companionship and reassurance
Managing Household and Financial Tasks
Caregivers often take on additional responsibilities such as:
- Handling grocery shopping and household chores
- Paying bills and managing finances
- Coordinating appointments and transportation
Advocating for Their Loved Ones
Caregivers act as advocates by:
- Communicating with doctors and ensuring proper medical care
- Making sure their loved one’s wishes are respected
- Researching available care options and resources
Challenges and Rewards of Caregiving
Common Challenges of Caregiving
Caregiving can be physically and emotionally demanding. Some of the most common challenges include:
- Burnout and exhaustion: Many caregivers neglect their own well-being, leading to burnout, stress, fatigue, and strain
- Financial strain: Unpaid family caregivers often have to reduce work hours or leave jobs entirely.
- Emotional stress: Watching a loved one struggle with illness or disability can be emotionally overwhelming.
- Limited personal time: Caregivers may find it difficult to maintain friendships, hobbies, or self-care, leading to loneliness and isolation.
The Rewards of Caregiving
Despite the challenges, caregiving is also incredibly fulfilling. Many caregivers find deep personal satisfaction in:
- Strengthening their relationships with loved ones
- Knowing they are making a difference in someone’s life
- Gaining patience, resilience, and a sense of purpose

Support and Resources for Caregivers
At FreedomCare, we recognize the dedication and hard work of caregivers and the burden that often comes with it. That’s why we provide comprehensive support and resources to help you navigate the challenges of caregiving with confidence. Whether you’re a family caregiver or a professional, we’re here to ensure you have the tools and assistance needed to succeed.
FreedomCare’s Support for Caregivers
As a caregiver with FreedomCare, you gain access to:
- Ongoing Training & Education: We offer guidance and training opportunities to help caregivers stay informed and confident in their roles.
- Dedicated Support Team: Our team is available to assist with questions, resources, and troubleshooting any caregiving challenges.
- Timely Payments & Benefits: We ensure caregivers are compensated fairly and on time, reducing financial stress.
Government and Non-Profit Assistance
In addition to FreedomCare’s support, several programs provide financial and practical assistance for caregivers:
- Medicaid and Medicare programs that cover home health services.
- AARP and the National Alliance for Caregiving offer guidance and caregiver support programs.
- Local Area Agencies on Aging (AAA) connect caregivers to community resources for additional help.
Respite Care and Support Groups
Caregiving can be demanding, and taking breaks is essential for your well-being. Many organizations, including FreedomCare, offer:
- Respite care services to provide temporary relief so you can rest and recharge.
- Online and in-person support groups, where caregivers can share experiences and receive encouragement from others in similar roles.
Financial and Legal Assistance
Caregivers should be aware of the financial and legal resources available to them:
- Tax credits and financial assistance programs that can help offset caregiving expenses.
Legal documents such as power of attorney, living wills, and healthcare directives to protect both the caregiver and their loved one’s interests.
How to Become a Caregiver
Becoming a Family Caregiver
If you are considering caring for a loved one, here’s how to prepare:
- Learn about their condition and specific care needs
- Set boundaries to maintain your own well-being
- Seek community resources for training and financial assistance
- Working directly with resources like FreedomCare
Becoming a Professional Caregiver
For those interested in caregiving as a career:
- Obtain certifications like CNA, HHA, or CPR training
- Gain experience through volunteer work or caregiving agencies
- Explore job opportunities in home care, assisted living, or hospitals
Conclusion
Caregiving is one of the most selfless and essential roles in society. Whether you’re a family member stepping up for a loved one or a professional providing care, your role is invaluable. At FreedomCare, we recognize the dedication and sacrifices that caregivers make every day. That’s why we empower family caregivers by offering support, resources, and financial assistance, allowing them to provide care for their loved ones while getting paid.
If you or someone you know is a caregiver, know that you’re not alone. Explore the resources available through FreedomCare, seek support, and prioritize your well-being. Caregivers make the world a more compassionate place—one act of care at a time. Let FreedomCare help you on your caregiving journey.
Do you have questions about becoming a caregiver or how to get paid as a family caregiver? Contact FreedomCare and speak with our support staff today.